PV-Bit
Verify the Bits that Fly®
PV-Bit
Verify the Bits that Fly®
User-driven verification of FPGA bitstreams
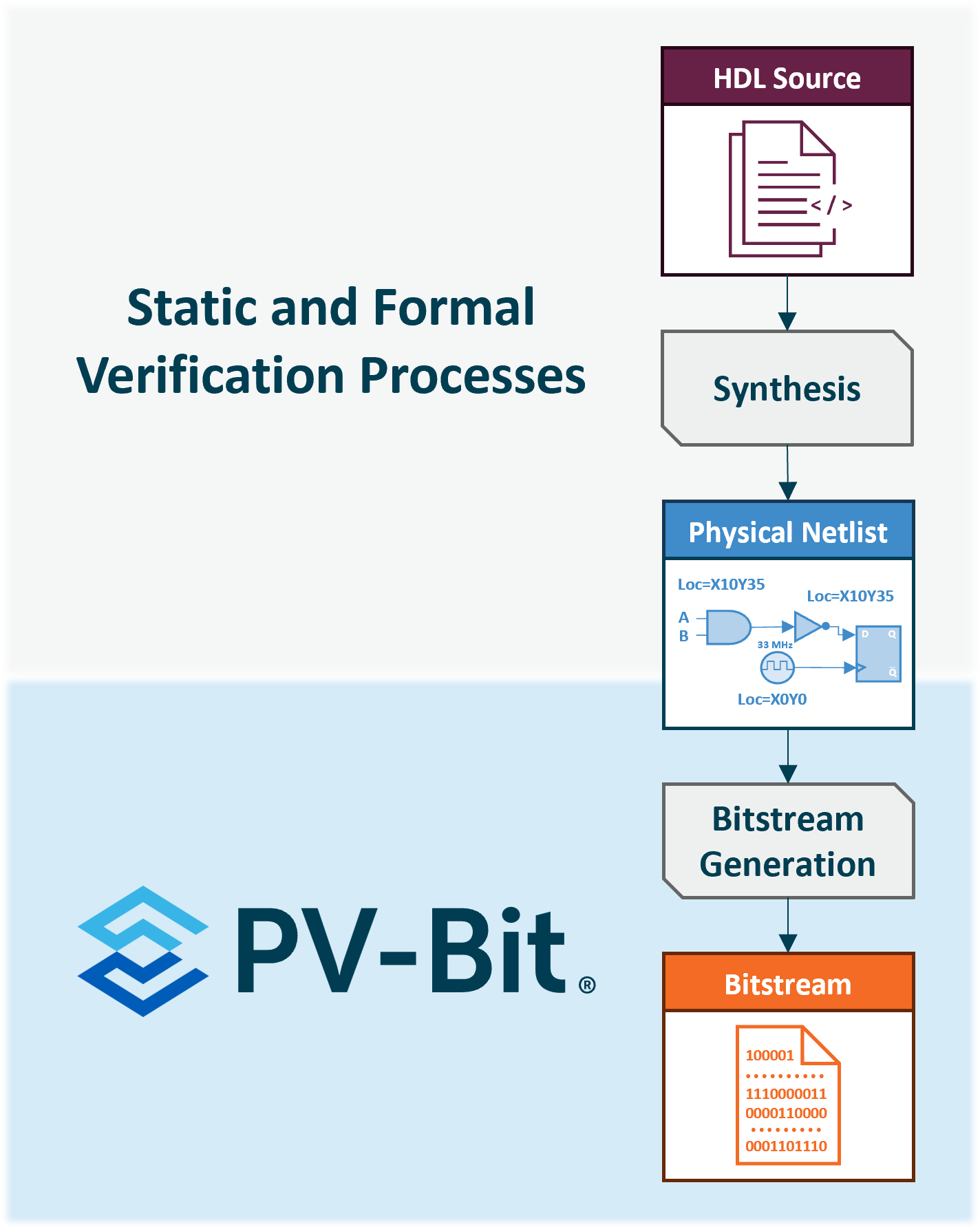
Enverité® PV-Bit® verification evaluates the equivalence of an FPGA bitstream and its physical netlist. The FPGA configuration bitstream is the only design representation that is actually deployed; however, existing verification tools are only able to verify publicly documented formats such as simulation netlists and HDL source code.
Graf Research® Corporation has leveraged our relationships with FPGA vendors along with a unique, patented technical approach to create Enverité PV-Bit verification, which allows the end-user to ensure their FPGA bitstream implementation matches that of the publicly documented and formally verifiable post place-and-route (PAR) simulation netlist.
Our unique, patented technical approach fills a gap in high assurance verification flows for security and functional safety by allowing an end-user to independently verify the functionality of their FPGA bitstream without reverse engineering.
PV-Bit verification respects FPGA vendor and third-party vendor IP
PV-Bit verification evaluates the contents of the vendor-proprietary bitstream while respecting FPGA vendor IP and third-party vendor IP. Instead of reverse-engineering the bitstream to HDL, PV-Bit verification performs an encapsulated comparison of the physical netlist and the bitstream. Once this process is complete, a report is generated for the user.
Enverité PV-Bit electronic design verification software is available in both downloadable and online forms.
PV-Bit verification helps you follow NSA guidance on FPGA assurance
The FPGA assurance guidelines released by NSA provide a list of mitigations against the introduction of Trojans during design development. One of these mitigations, Select a proof process, helps protect against an adversary that compromises the design cycle. The mitigation description is as follows:
Use logical equivalency checking to the greatest extent possible. Equivalency checking is used to prove the tools did not modify the logic or configuration settings. To do this, the final bitstream is compared to the originating application HDL to demonstrate they are logically equivalent with no extraneous logic in the final format. This approach confirms Trojans were not inserted during the implementation steps. This check also confirms configuration settings are maintained and not altered.
PV-Bit verification helps you comply with this guideline by allowing you to verify the contents of your bitstreams against the final placed-and-routed (PAR) netlist generated from your build tools. If this post-PAR netlist is then compared to the source HDL using a commercial logic equivalence checking tool, the NSA suggested best practice is met.
More Information
Use the Request Documents form to request the PV-Bit whitepaper as well as other relevant documents.
If you’d like to contact us about using PV-Bit verification, or if you wish to see a product demonstration or have a product support question, contact us.

PV-Bit Delta
Accelerating FPGA Delta Verification
PV-Bit Delta
Accelerating FPGA Delta Verification
bitstream equivalence checking accelerates recertification of FPGA designs in highly regulated industries by providing evidence that the ECO change was the only alteration to the certified bitstream.
Delta Verification of an Engineering Change Order
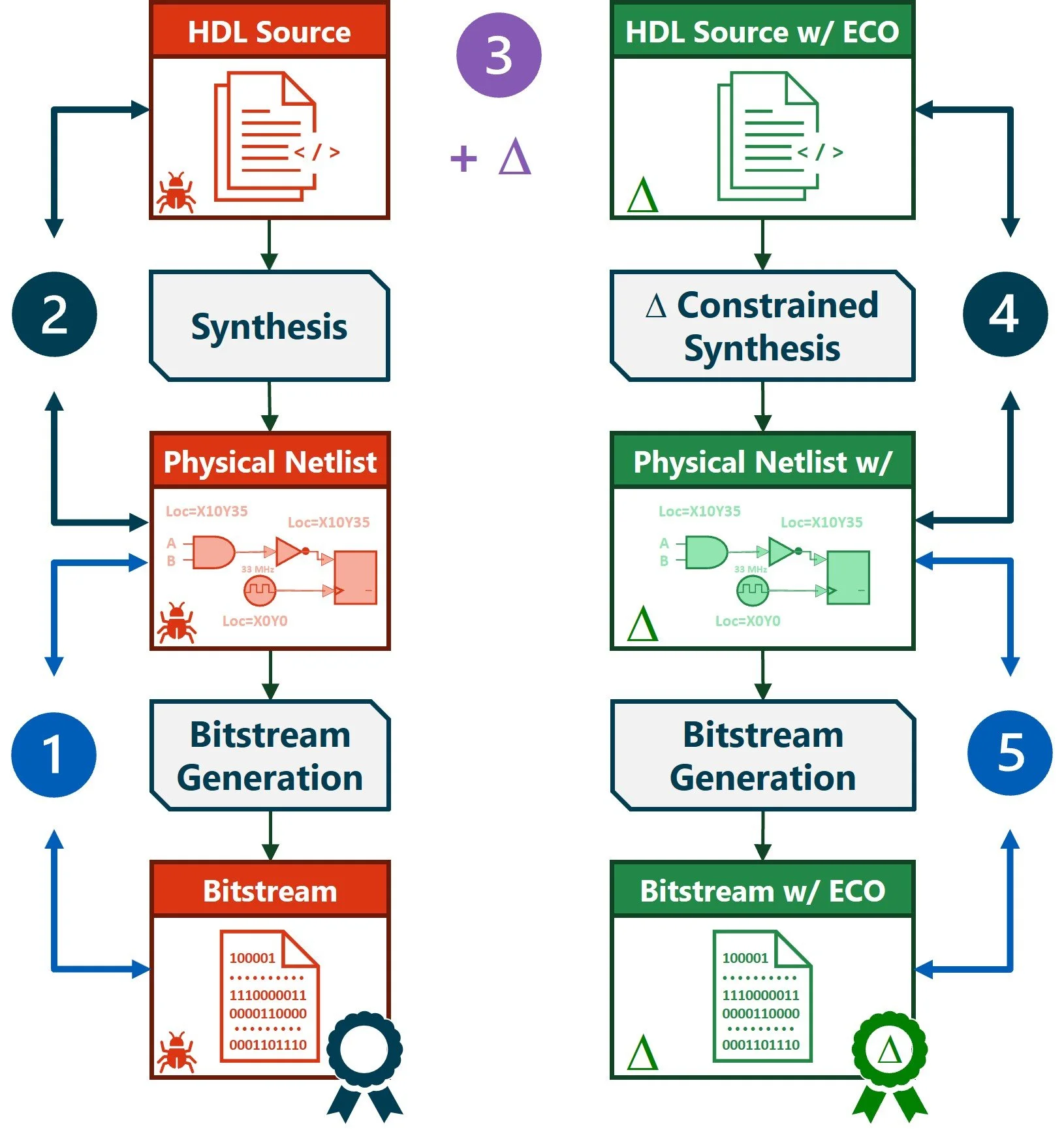
Recertification of updates to FPGA-based systems in heavily regulated industries can be as expensive and time consuming as the original certification. Enverité® PV-Bit® Bitstream Equivalence Checking (BEC) enables a delta verification flow to accelerate the process by providing evidence that the changes between the original bitstream and the bitstream fixed by an Engineering Change Order (ECO) are well defined and minimal. Enverité PV-Bit BEC paired with a logic equivalence checking (LEC) tool can prove that the HDL-described ECO change was the only logical alteration to the certified bitstream. Paired with timing and power re-analysis on the physical netlist, this may reduce and focus recertification testing.
Delta Verification Process
A tool chain may be established to verify the relationship between the certified bitstream and the bitstream with the ECO change, exposing and formally defining the differences between them.
Bitstream to physical netlist equivalence check of the original design with Enverité PV-Bit BEC
Physical netlist to HDL source equivalence check of the original design with LEC software
Implementation of the ECO (Delta) at the HDL level
Synthesis of the Delta HDL source; logical equivalence check with the Delta physical netlist; timing and power analysis of the Delta physical netlist using original constraints
Bitstream synthesis of the Delta physical netlist and a physical and functional equivalence check with the Delta bitstream using Enverité PV-Bit verification
Once complete, the process proves the Delta is the only logical change between the original and updated bitstreams.
Request Enverité PV-Bit Delta Verification Whitepaper
PV-Bit Support
PV-Bit Support
Enverité PV-Bit 1.2025.1 Support
Operating Systems and FPGA Vendor Tools
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 64-bit, 22.04 LTS 64-bit, and 24.04 LTS 64-bit
All AMD Vivado versions up to 2024.2.x that support the given OS
RedHat Enterprise Linux 8.10 64-bit
AMD Vivado 2024.2.x
Device Support
AMD Artix 7 FPGA
XC7A200T
AMD UltraScale FPGA
All Kintex and Virtex Devices
AMD UltraScale+ FPGA
All Kintex and Virtex devices excluding XCKU19P, XCVU19P, and Virtex 5G and HBM parts
AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC Devices
All devices excluding XCZU3TCG, XCZU3TEG, and XAZU3TEG
AMD Zynq UltraScale+ RFSoC Devices
All devices excluding XCZU63DR and XCZU64DR
Upcoming Enverité PV-Bit 1.2026.1 Support
Additional Linux operating systems, including versions of CentOS, RedHat, Rocky, and SUSE
Select AMD Versal Prime devices, additional AMD UltraScale+ devices, and all AMD Artix 7 devices
Contact us for more information about current and future support.
Coming Soon
Altera, Lattice, and Microchip logos are trademarks of their respective corporations
This page contains forward-looking information about Graf Research technologies and is subject to change.